Interest reserves are a key component of hard money loans, providing borrowers with a solution to manage interest payments during the course of the loan. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of interest reserves in hard money loans, shedding light on their purpose, mechanics, and benefits. By gaining a clear understanding of how interest reserves function, borrowers will be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions when navigating the realm of hard money lending.
Overview of Hard Money Loans
Definition of hard money loans
Hard money loans are short-term, asset-based loans that are typically used by real estate investors and individuals who cannot qualify for traditional bank loans. Unlike traditional loans, hard money loans are not based on the borrower’s creditworthiness but rather on the value of the property being used as collateral.
Purpose of hard money loans
The purpose of hard money loans is to provide borrowers with quick access to funding for real estate projects. These loans are often used for fix-and-flip projects, property acquisitions, and construction projects where time is of the essence. Hard money loans offer flexibility and allow borrowers to take advantage of investment opportunities that may not be available through traditional financing channels.
Understanding Interest Reserves
Definition of interest reserves
Interest reserves are a mechanism used in hard money loans to ensure consistent payment of interest to the lender. These reserves are typically set aside at the time of loan origination and are held in a separate account. The borrower makes regular interest payments from this account, rather than from their own personal funds.
Purpose of interest reserves
The purpose of interest reserves is to mitigate the risk for the lender and provide a safety net for the borrower. By setting aside funds specifically for interest payments, the borrower ensures that the lender receives timely payments even if the project experiences unforeseen challenges. Interest reserves also give the borrower greater flexibility in managing their cash flow during the loan term.
How interest reserves are calculated
Interest reserves are calculated based on the anticipated interest payments over the loan term. The lender evaluates the project’s cash flow projections and determines the amount of reserves required. This calculation takes into consideration the interest rate, the loan amount, and the expected duration of the loan.
Benefits of Interest Reserves
Ensures consistent payment of interest
By using interest reserves, borrowers can ensure that interest payments are made consistently and on time. This helps build trust and credibility with the lender, which can be beneficial for future borrowing needs.
Provides a safety net for borrowers
Interest reserves provide a safety net for borrowers by ensuring that they have funds set aside specifically for interest payments. This mitigates the risk of defaulting on the loan and offers peace of mind to both borrower and lender.
Allows for greater flexibility
Interest reserves give borrowers greater flexibility in managing their cash flow. With the funds set aside for interest payments, borrowers can allocate their remaining funds towards other project expenses or unforeseen costs that may arise during the loan term.
Considerations for Lenders
Assessing the borrower’s ability to repay
Lenders must thoroughly assess the borrower’s ability to repay the loan, including the interest reserves. This includes evaluating the borrower’s credit history, their experience in real estate investing, and their cash flow projections for the project. By conducting a comprehensive assessment, lenders can determine if the borrower has the capacity to maintain the interest reserves.
Determining the appropriate amount for interest reserves
Lenders must carefully calculate the appropriate amount for interest reserves based on the projected interest payments. It is essential to consider any potential risks or challenges that could impact the project’s cash flow. Setting aside too little may expose the lender to additional risk, while setting aside too much could unnecessarily tie up the borrower’s funds.
Monitoring and managing interest reserves
Lenders need to keep a close eye on the interest reserves throughout the loan term. This includes regularly monitoring the borrower’s interest payments and ensuring that the reserves are sufficient to cover the interest obligations. Effective communication and documentation are key to minimizing the risk of default and addressing any potential issues that may arise.
Application of Interest Reserves
How interest reserves are used in hard money loans
Interest reserves are applied in hard money loans by creating a separate account specifically for the interest payments. The borrower makes regular interest payments from this account, which is funded by the reserves. This ensures that the lender receives their interest payments consistently throughout the loan term.
Case study examples
To illustrate how interest reserves work in hard money loans, consider the following case study examples:
-
Fix-and-flip project: In this scenario, a real estate investor borrows funds through a hard money loan to purchase a distressed property. The interest reserves are used to make monthly interest payments while the borrower renovates the property. Once the property is sold, the borrower repays the loan, including the interest reserves.
-
Construction project: A developer obtains a hard money loan to fund a construction project. The interest reserves are used to make interest payments during the construction phase, as there may be delays in generating revenue from the project. Once the property is completed and generates income, the borrower repays the loan in full.
Potential Drawbacks of Interest Reserves
Higher upfront costs for borrowers
Interest reserves increase the upfront costs for borrowers, as they must set aside funds specifically for interest payments. This can be a significant financial burden, especially for borrowers with limited resources or for projects with tight budgets.
Limited availability for certain borrowers
Interest reserves may not be available to all borrowers, especially those with lower credit scores or limited experience in real estate investing. Some lenders may require borrowers to have a certain level of financial stability and a proven track record before approving a loan with interest reserves.
Impact on loan terms and conditions
The inclusion of interest reserves in a hard money loan may affect the overall terms and conditions of the loan. Lenders may charge higher interest rates or impose stricter repayment terms to offset the potential risks associated with the use of interest reserves.
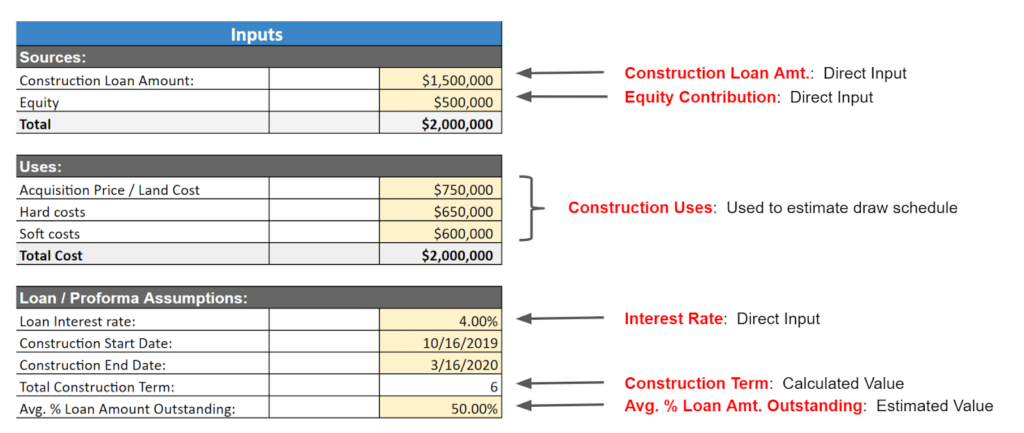
Comparing Interest Reserves to Traditional Loan Structures
Differences in interest payment structures
In traditional loan structures, borrowers make interest payments using their own funds. However, in hard money loans with interest reserves, borrowers make interest payments from the reserves set aside specifically for that purpose. This allows borrowers to manage their cash flow more efficiently.
Advantages and disadvantages of interest reserves
Interest reserves offer advantages such as ensuring consistent payment of interest and providing a safety net for borrowers. However, they also come with drawbacks such as higher upfront costs and limited availability for certain borrowers. It is essential for borrowers to carefully weigh these factors when considering the use of interest reserves in their loan structure.
Tips for Borrowers
Understanding the terms of the interest reserves
It is crucial for borrowers to thoroughly understand the terms and conditions associated with the interest reserves. This includes knowing the amount required, the method of calculation, and any potential penalties or restrictions related to the reserves. Clear communication with the lender is key to avoid misunderstandings or surprises during the loan term.
Planning for repayment of interest reserves
Borrowers should develop a comprehensive plan for repaying the interest reserves. This includes considering the project timeline, expected cash flow, and any other financial obligations. By planning ahead, borrowers can ensure that they have the necessary funds available to repay the interest reserves in a timely manner.
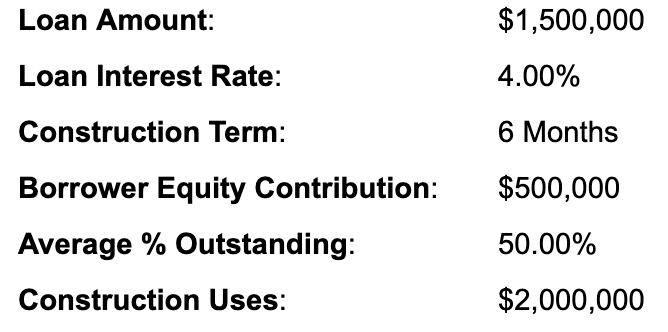
Tips for Lenders
Evaluating the risks and benefits of interest reserves
Lenders should carefully evaluate the risks and benefits associated with interest reserves before incorporating them into a loan structure. This includes assessing the borrower’s financial stability and project feasibility. Conducting thorough due diligence and risk assessment can help lenders make informed decisions and minimize potential losses.
Working with borrowers to ensure successful repayment
Effective communication and collaboration with borrowers are crucial for successfully managing interest reserves. Lenders should establish clear expectations, provide guidance on managing cash flow, and regularly review the borrower’s progress. By working together, lenders and borrowers can increase the likelihood of successful repayment.
Conclusion
Summary of how interest reserves work in hard money loans
Interest reserves play a significant role in hard money loans, providing stability and flexibility for both borrowers and lenders. By setting aside funds specifically for interest payments, borrowers can ensure consistent payments while having the flexibility to manage other project expenses. Lenders benefit from reduced risk and increased confidence in the borrower’s ability to repay.
Considerations for borrowers and lenders
Borrowers must carefully consider the additional upfront costs and potential limitations that come with using interest reserves. They should fully understand the terms and plan for repayment accordingly. Lenders, on the other hand, need to assess the borrower’s ability to repay, determine appropriate reserve amounts, and monitor the reserves throughout the loan term.
In conclusion, interest reserves are a valuable tool in the world of hard money loans, offering benefits to both borrowers and lenders. However, it is essential for all parties involved to thoroughly understand the implications and carefully consider whether interest reserves are the right fit for their specific situation.






